What Happens When Gases Cant Leave the Ztmosphere Due to the Greenhouse Effect
› en español
Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid-20th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps oestrus radiating from Earth toward infinite.
Certain gases in the temper block rut from escaping. Long-lived gases that remain semi-permanently in the temper and do not respond physically or chemically to changes in temperature are described as "forcing" climatic change. Gases, such as water vapor, which reply physically or chemically to changes in temperature are seen as "feedbacks."
Gases that contribute to the greenhouse consequence include:
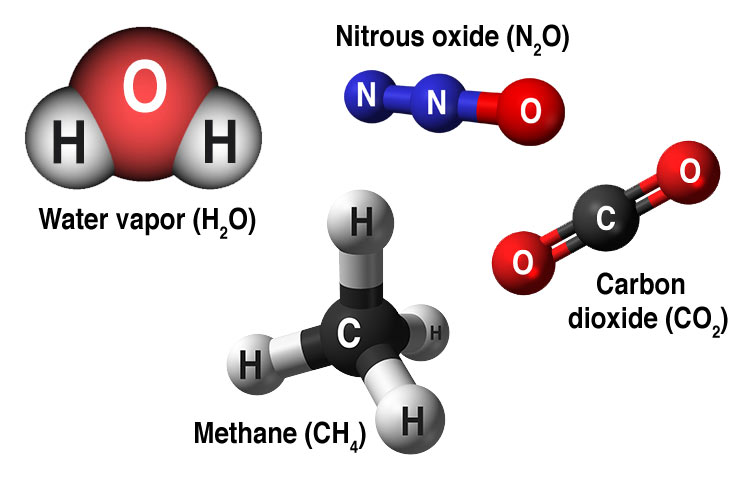
- Water vapor. The most arable greenhouse gas, simply importantly, it acts as a feedback to the climate. Water vapor increases as the Earth'south temper warms, but so does the possibility of clouds and atmospheric precipitation, making these some of the most important feedback mechanisms to the greenhouse effect.
- Carbon dioxide (COii). A minor only very important component of the atmosphere, carbon dioxide is released through natural processes such every bit respiration and volcano eruptions and through man activities such as deforestation, land use changes, and burning fossil fuels. Humans accept increased atmospheric COtwo concentration by 48% since the Industrial Revolution began. This is the almost important long-lived "forcing" of climate change.
- Methane. A hydrocarbon gas produced both through natural sources and man activities, including the decomposition of wastes in landfills, agriculture, and specially rice tillage, likewise as ruminant digestion and manure management associated with domestic livestock. On a molecule-for-molecule basis, methane is a far more active greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide, simply also one which is much less abundant in the atmosphere.
- Nitrous oxide. A powerful greenhouse gas produced past soil cultivation practices, especially the use of commercial and organic fertilizers, fossil fuel combustion, nitric acrid production, and biomass called-for.
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Synthetic compounds entirely of industrial origin used in a number of applications, only now largely regulated in product and release to the atmosphere by international agreement for their ability to contribute to destruction of the ozone layer. They are also greenhouse gases.


On Earth, human activities are changing the natural greenhouse. Over the concluding century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). This happens because the coal or oil called-for process combines carbon with oxygen in the air to brand COtwo. To a bottom extent, the clearing of state for agriculture, industry, and other human activities has increased concentrations of greenhouse gases.
The consequences of irresolute the natural atmospheric greenhouse are difficult to predict, merely some furnishings seem likely:
- On average, World volition become warmer. Some regions may welcome warmer temperatures, but others may not.
- Warmer conditions will probably lead to more evaporation and precipitation overall, but individual regions will vary, some condign wetter and others dryer.
- A stronger greenhouse effect will warm the ocean and partially melt glaciers and ice sheets, increasing sea level. Bounding main water also volition expand if it warms, contributing further to sea level rising.
-
Outside of a greenhouse, higher atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels can take both positive and negative effects on crop yields. Some laboratory experiments suggest that elevated CO2 levels can increase found growth. Withal, other factors, such every bit changing temperatures, ozone, and water and nutrient constraints, may more than counteract whatsoever potential increase in yield. If optimal temperature ranges for some crops are exceeded, before possible gains in yield may exist reduced or reversed birthday.
Climate extremes, such every bit droughts, floods and farthermost temperatures, can pb to crop losses and threaten the livelihoods of agricultural producers and the food security of communities worldwide. Depending on the crop and ecosystem, weeds, pests, and fungi tin also thrive nether warmer temperatures, wetter climates, and increased CO2 levels, and climate change will likely increase weeds and pests.
Finally, although rising CO2 can stimulate establish growth, research has shown that it can likewise reduce the nutritional value of most nutrient crops past reducing the concentrations of poly peptide and essential minerals in near plant species. Climate change can cause new patterns of pests and diseases to emerge, affecting plants, animals and humans, and posing new risks for food security, nutrient safe and human being health. two
The Role of Human Activity
In its Fifth Assessment Report, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate change, a group of 1,300 independent scientific experts from countries all over the world under the auspices of the United Nations, concluded there's a more than 95 per centum probability that human activities over the past 50 years have warmed our planet.
The industrial activities that our modern civilisation depends upon have raised atmospheric carbon dioxide levels from 280 parts per million to about 417 parts per meg in the last 151 years. The panel as well ended there's a better than 95 pct probability that human-produced greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide have acquired much of the observed increase in Earth's temperatures over the past 50-plus years.
The panel's full Summary for Policymakers written report is online at https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/02/ipcc_wg3_ar5_summary-for-policymakers.pdf.
Solar Irradiance
The corporeality of solar energy that Earth receives has followed the Sun's natural 11-year cycle of small ups and downs with no internet increase since the 1950s. Over the same period, global temperature has risen markedly. It is therefore extremely unlikely that the Lord's day has caused the observed global temperature warming trend over the past half-century. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
It'southward reasonable to assume that changes in the Sun's energy output would cause the climate to alter, since the Sun is the fundamental source of free energy that drives our climate system.
Indeed, studies bear witness that solar variability has played a role in past climate changes. For example, a decrease in solar activity coupled with an increase in volcanic activity is thought to take helped trigger the Footling Ice Historic period between approximately 1650 and 1850, when Greenland cooled from 1410 to the 1720s and glaciers avant-garde in the Alps.
But several lines of evidence prove that current global warming cannot be explained by changes in energy from the Sun:
- Since 1750, the average corporeality of free energy coming from the Sunday either remained constant or increased slightly.
- If the warming were caused by a more active Sun, then scientists would look to see warmer temperatures in all layers of the atmosphere. Instead, they have observed a cooling in the upper temper, and a warming at the surface and in the lower parts of the temper. That'south because greenhouse gases are trapping heat in the lower temper.
- Climate models that include solar irradiance changes can't reproduce the observed temperature trend over the past century or more than without including a rise in greenhouse gases.
References
-
IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, 2014
United States Global Alter Research Program, "Global Climate change Impacts in the United States," Cambridge University Printing, 2009
Naomi Oreskes, "The Scientific Consensus on Climate Alter," Science 3 December 2004: Vol. 306 no. 5702 p. 1686 DOI: ten.1126/scientific discipline.1103618
-
U.South. Environmental Protection Agency: "Climate Impacts on Agronomics and Food Supply"
-
Mike Lockwood, "Solar Change and Climate: an update in the calorie-free of the current infrequent solar minimum," Proceedings of the Royal Gild A, 2 December 2009, doi 10.1098/rspa.2009.0519;
Judith Lean, "Cycles and trends in solar irradiance and climate," Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change, vol. i, January/February 2010, 111-122.
Source: https://climate.nasa.gov/causes/
0 Response to "What Happens When Gases Cant Leave the Ztmosphere Due to the Greenhouse Effect"
Post a Comment